“Fast, Good or Cheap”
Mega projects represent some of the most ambitious and complex initiatives undertaken worldwide. With budgets running into the £billions and timescales stretching over decades, these projects are critical for economic development and societal progress, with examples including HS2, the Elizabeth Line and Hinkley Point power station. Frequently plagued by cost overruns, schedule delays, and scope creep – issues encapsulated in the Iron Triangle of Project Management.
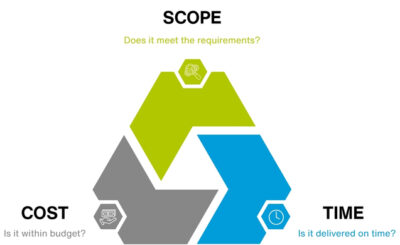
The Iron Triangle concept was introduced by Dr. Martin Barnes in the 1960s, to illustrate the trade-offs between Scope, Time, and Cost in project management, emphasising that optimising one constraint often impacts the other two. Managing these factors effectively is essential to delivering mega projects successfully:
- Scope: Defines the project’s objectives, deliverables, quality expectations and alignment with stakeholder requirements.
- Time: Represents the schedule and deadlines, often rigid in large-scale projects, requiring precise coordination and active management.
- Cost: Encompasses the financial resources required, from materials to labour, necessitating rigorous oversight and forecasting.
The challenge? When one of these constraints shifts, it inevitably impacts the other two. Expanding the scope often requires more time and cost, while reducing costs may limit scope or extend deadlines. This constant competition is a major reason mega projects often face difficulties , with a recent study finding 80% of projects exceed their initial budget, 90% face delays in meeting their original deadlines and 70% experience scope changes or expansions. (Flyvbjerg, 2014)
Common Issues in Mega Projects
Despite their importance, mega projects frequently encounter recurring challenges:
- Cost Overruns – Nearly all mega projects exceed their initial budgets due to poor forecasting, planning, and lack of control (Flyvbjerg, 2017). For example, the London Crossrail project saw costs soar by £4 billion beyond its original estimate.
- Schedule Delays – While fixed deadlines are essential, inflexible timelines can hinder effective delivery. HS2 has already encountered multiple setbacks due to regulatory hurdles and complex construction challenges.
- Scope Creep – Changing stakeholder demands can expand project requirements, increasing costs. The Manchester Metrolink expansion, originally planned at £520 million, saw costs rise to £870 million due to additional route extensions.
- Stakeholder Complexity – Large projects involve multiple stakeholders, including governments, private investors, contractors, and regulatory bodies, often with conflicting interests and priorities.
- Manage and Control – Traditional management methods struggle to adapt to the evolving nature of large projects, which require a more flexible approach to manage and control the change and challenges Mega Projects face.
How can we mitigate these issues?
Best practice solutions to overcome these challenges include:
- Accurate Forecasting & Planning – Leverage historical performance data to create reliable cost and timeline estimates, minimising uncertainty. This enables us to create joined up and meaningful programmes, allowing meaningful action down to the daily plan.
- Active Management – Take a proactive, hands-on approach to address challenges quickly and keep the project on track.
- Short Interval Control – KPI and performance driven through implementation of daily huddles and regular reviews to ensure continuous focus, swiftly resolve issues, and manage scope changes.
- Proactive Risk Management – Capture issues from frontline workers to identify risks early and establish contingency plans to mitigate challenges before they escalate.
- Stakeholder Engagement – Maintain ongoing communication and alignment with stakeholders to ensure shared expectations and drive project success.
These interventions enable you to navigate the challenges of mega projects effectively, ensuring delivery on time, within scope, and on budget, whilst generating long term client value and advancing the economic and societal progress these initiatives are designed to achieve.

